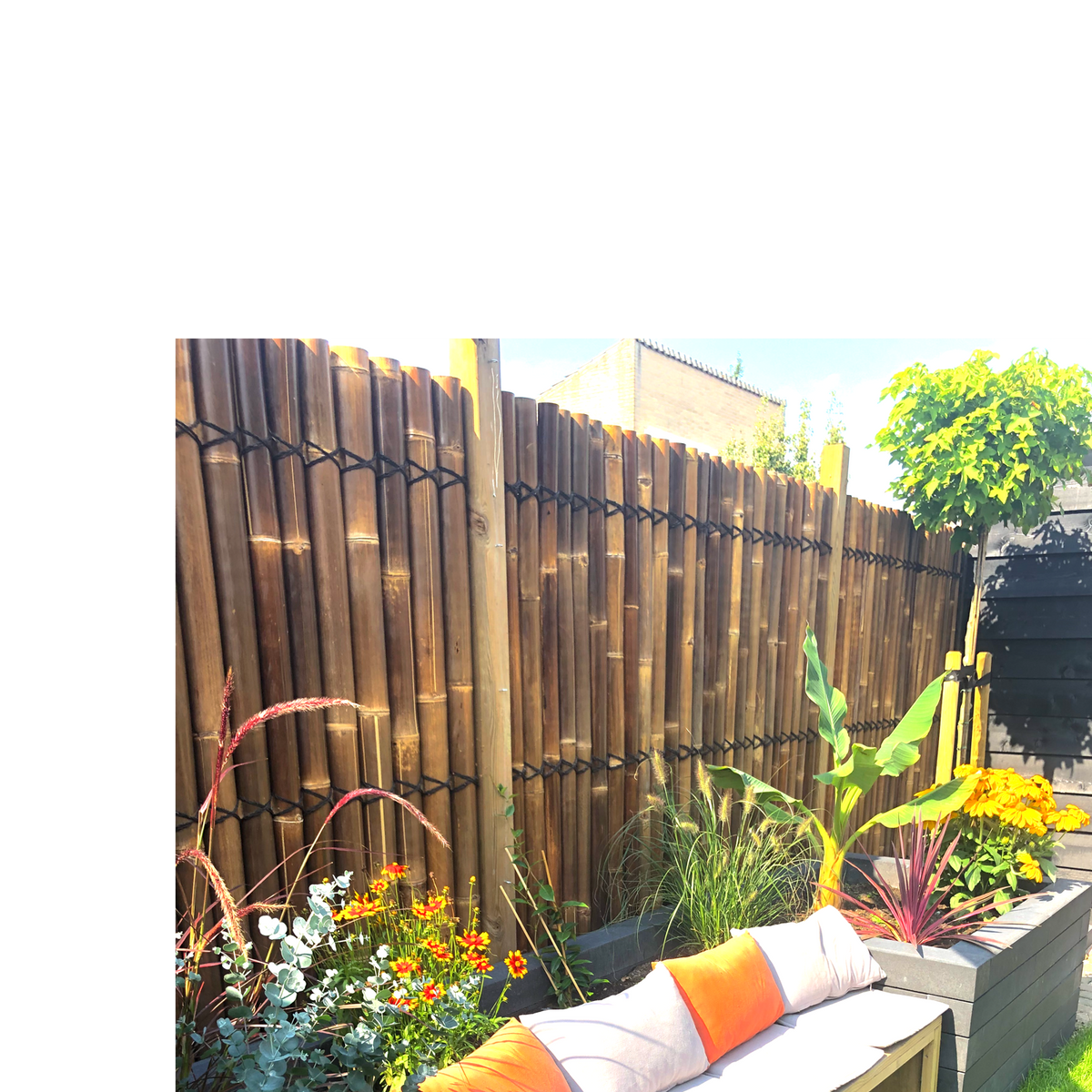
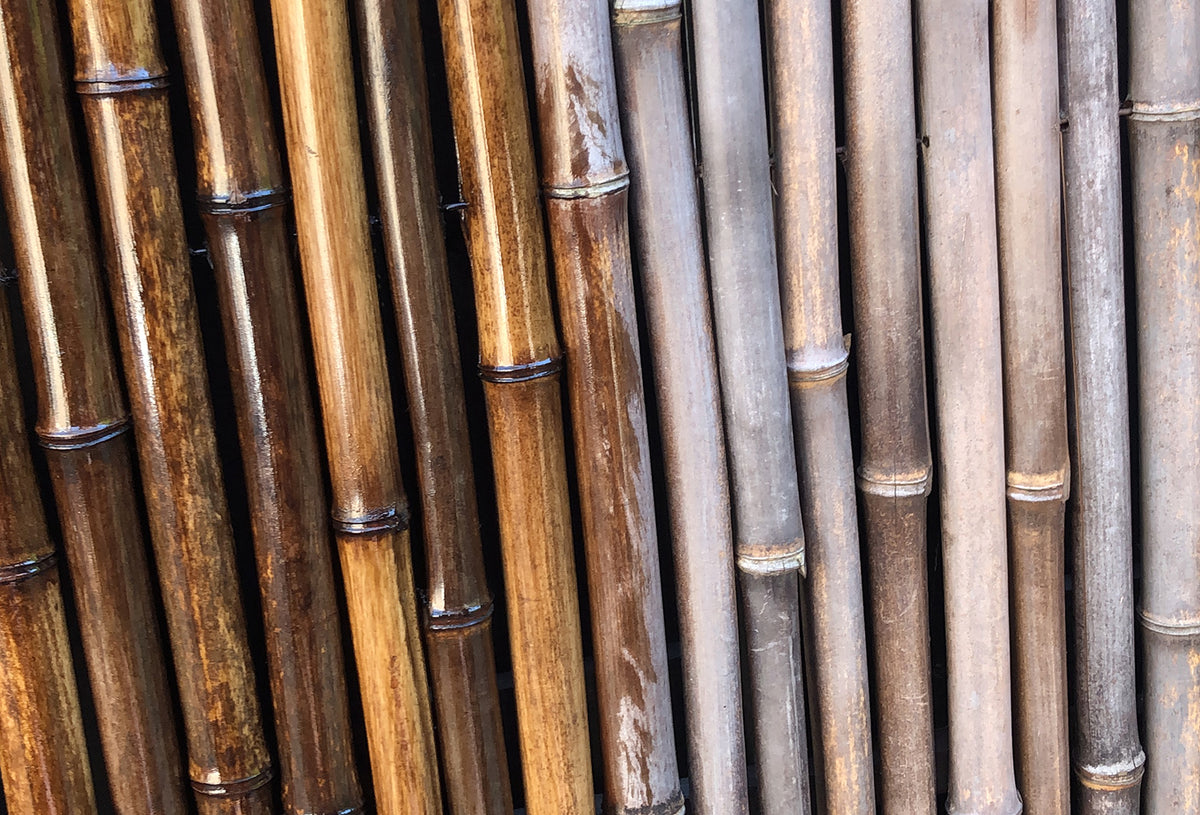
Protect the forest, build with bamboo
Bamboo is known as an incredibly sustainable and environmentally friendly product. But why is bamboo environmentally friendly?
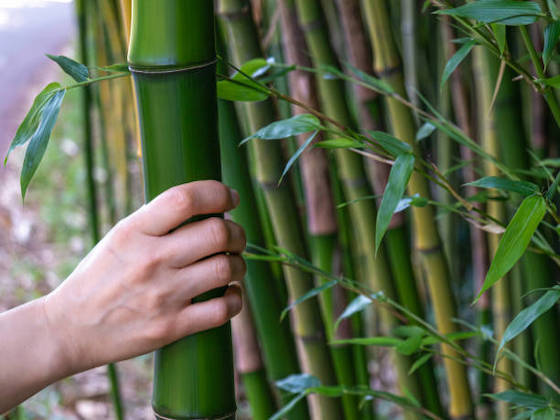
Bamboo versus wood
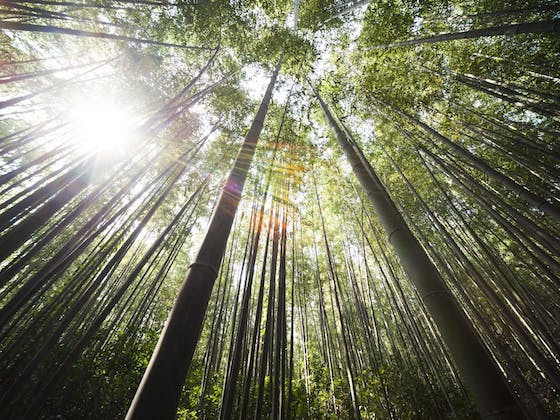
Bamboo grows quickly and there are more than 1,500 different species of bamboo, 50 of which are suitable as building materials. Because bamboo is a member of the grasses (Gramineae), it sometimes shoots up to 30 feet from the ground within six months. The largest known bamboo species is Dendrocalamus.
In bamboo plantations, only the mature bamboo plants are harvested, the rest is left to develop further. When harvesting, care is taken to leave enough of the stem so that a new bamboo stem can grow back. This then has the nutrients and root system of the harvested bamboo, which of course only benefits the new bamboo. When a bamboo seed is planted, it forms a clump under the soil. This clump can absorb up to 2 tons of CO2 over the course of 7 years. In comparison, a deciduous tree absorbs only 1 ton of CO2 in 40 years.



Bamboo has a rotation period of seven years. For woody species, it is 30 years. So that's already a big difference. The actual record time is 1.22 meters per day. Bamboo has the characteristics of hardwood, but grows faster than softwood. Every year, more than 13 million hectares of forest are cut down. That's 1140 soccer fields per hour. Of course, forests are also planted, but the net annual loss of forest is more than 7 million hectares, which is more than twice the area of Belgium. If these forests were not cut down, up to a quarter less CO2 would be released into the air.
The use of bamboo significantly reduces the greenhouse effect and climate change. Bamboo absorbs greenhouse gases. The carbon dioxide (CO2) released by bamboo releases 35% more oxygen into the atmosphere than an equivalent hardwood species. This is due to its high growth rate and photosynthesis. Climate change has been a concern for several years, so bamboo could be considered as a certified solution. Bamboo is also suitable for biomass production as it provides the second highest biomass on earth.
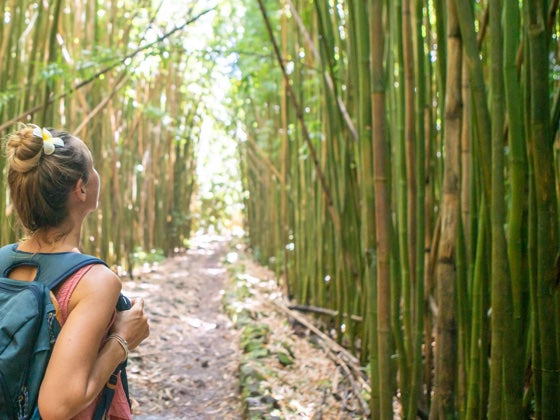
Bamboo in nature
Bamboo also plays an important role in regulating water quantity and quality. Because of the water absorption system in the trunk of bamboo, it acts almost like a water pump. When it rains, it absorbs water, which is released back into the earth when it is dry. One hectare of bamboo can store up to 30,000 liters of water. This allows bamboo to grow in difficult conditions where other plants cannot. This also has a positive effect on soil quality, as the roots hold the soil together. This also reduces the risk of landslides and erosion near rivers.
Bamboo is also an important component of many ecosystems with great biodiversity. Worldwide, there are several animals that use bamboo for food and shelter. A well-known example is the giant panda (from China), but also the red panda (China), the mountain gorilla (Uganda), the halblemur (Madagascar), the baloogle cat (Ethiopia) and the Gracilinanus agilis (South America). Apart from these animals, many birds also benefit from bamboo. Thus, planting bamboo can quickly create the right conditions for these species.
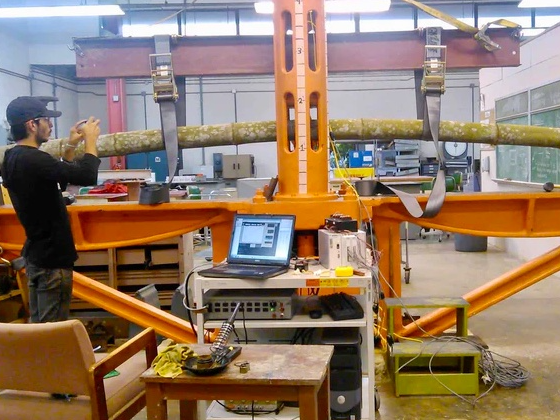
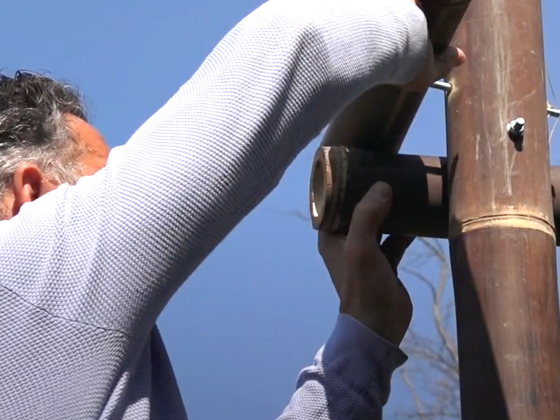
Bamboo in structures
In Europe, we use bamboo in gardens and as a finishing material. But why is it not more commonly used as a building material in Europe? After all, bamboo is one of the strongest building materials in the world. It has a tensile strength of 28,000 inches per square millimeter compared to 23,000 inches for steel. You learn from nature when you study the structure of bamboo, because nature builds much more efficiently than we humans do. We build rigidly, but with less rigid dampers and elastic springs that look like the building system of a bamboo trunk, we can build less rigidly.
For example, we also import the Guadua species of bamboo. These are even stronger (but also lighter) than steel, making them very suitable for structural applications. You can see more about this in this video. You can read more about bamboo in construction here.



Applications of bamboo
Bamboo poses no environmental problems when grown. It is a renewable resource that does not deplete. The key is that by laminating bamboo, anything made from wood can be made from bamboo. Once bamboo fibers are stripped of their natural sugars and impregnated with salts, they become immune to insects. This increases the lifespan of bamboo logs to 50 years or more. However, this requires that they are not used in direct contact with the sun, rain or soil. However, for sustainable outdoor use of bamboo canes, additional care by the end user is required.
Bamboo can be used in its natural form as well as a processed product for many different applications. Bamboo fibers are soft and durable when woven. Bamboo clothing is very durable and is said to have antibacterial and antifungal properties that prevent sweat odor. Because of its environmental friendliness and versatility, bamboo is increasingly being chosen as a raw material for various applications. Examples include clothing, furniture, decking, fencing, bread drums, toothbrushes and packaging materials, construction and more. Other products in the luxury segment include a bamboo steering wheel and the interior of an (expensive) car, or electronic products such as a bamboo phone case, bamboo computer mice and keyboards, or bamboo headphones.



In short, bamboo is so popular because of its environmental friendliness and special properties. Because of its versatility, it can be used in many different areas.